Google’s newest “useful content material” algorithm replace ended on September 15. It was disastrous for a lot of websites.
In case your website misplaced natural visitors, right here’s the right way to get well.
1. Consider Losses
“Useful content material” is now a sitewide issue per Google’s Search Central tips:
Any content material — not simply unhelpful content material — on websites decided to have comparatively excessive quantities of unhelpful content material total is much less more likely to carry out properly in Search.
Therefore the whole website suffers if Google claims in depth unhelpful content material, making it tough to determine which pages to give attention to. Thus estimating the general impression is step one to figuring out the scope. If it’s sitewide, rework your complete content material technique.
Google’s Search Console identifies the pages that misplaced natural visitors.
- Go to the “Efficiency > Search outcomes” report.
- Select “Evaluate” within the “Date” filter.
- Select “Evaluate final 28 days to earlier interval” and click on “Apply.”
- Click on on “Pages” and the “Clicks Distinction” column header to type by visitors adjustments.
Export the desk to a spreadsheet for a greater view of what number of pages misplaced visitors.
2. Establish Competing Pages
Sufficient time has handed to determine exterior pages with visitors good points. Decide the search queries with the most important rating drops and discover pages that gained what you misplaced. Instruments resembling Ahrefs, Semrush, Sitechecker, and others can produce this data. Search for URLs with significant rating adjustments for every question.
Spyfu also can assist. It gives a helpful graphical illustration of search rankings — URLs that elevated and decreased for a given question.
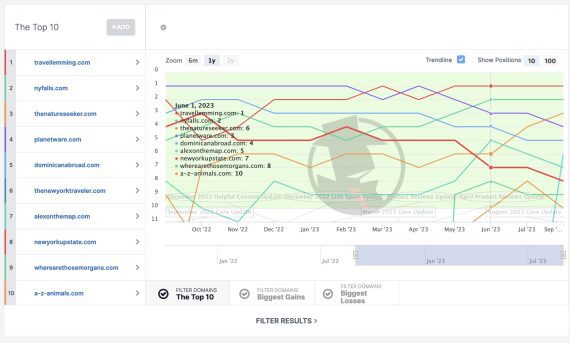
A graph in Spyfu exhibits URLs with good points and losses in rankings for a given question. Click on picture to enlarge.
Google’s definition of unhelpful content material is, properly, not very useful. It’s content material with “little worth, low-added worth or is in any other case not notably useful to folks.” Analyzing profitable competitor pages may present clues. For every web page, ask:
- Is the content material extra broad or extra particular than yours?
- How is it structured?
- Does it include key phrases all through the web page?
- Is there a desk of contents and jump-to hyperlinks?
- Is there social proof — resembling shares or feedback — on the web page?
- Is there an writer byline that hyperlinks to a bio?
- Does it include Schema.org markup? How a lot?
- Does the content material hyperlink to trusted sources?
- Does it embrace pictures or movies?
- Does it embrace information, tendencies, or stats?
- Is it new or freshly up to date?
- Does it completely deal with the question with FAQs and definitions as wanted?
- Does it embrace associated entities — respected manufacturers, merchandise, folks, locations — or ideas that yours doesn’t? Textual content Optimizer might help determine these. It can analyze URLs in your website and a competitor’s, scoring each primarily based on the variety of associated ideas and recognized entities. inLinks gives a helpful entity checker, too.
- Has the location gained rankings seemingly out of nowhere? Google’s useful content material makes an attempt to search out “hidden gems,” low-ranking websites with wonderful data. Discovering a kind of may inform Google’s priorities.
- Does the writer’s bio state her expertise and experience related to the article?
The useful content material algorithm ranks pages for every question primarily based on how searchers may benefit. Some queries require definitions and solutions to frequent questions. Others search clear steps or directions to unravel an issue or process. Your analysis goals to search out what Google discovered notably helpful for every question.
Use the Wayback Machine to see a web page’s earlier content material. Maybe it now comprises higher information, explanations, or sections that set off the useful content material filters.
3. Present Fewer Adverts, Popups
Fairly a couple of discussions on search engine marketing boards recommend that closely monetized websites have misplaced essentially the most rankings, particularly these with intrusive interstitials or extreme adverts.
“Intrusive interstitials” are popups that block many of the display. These are sometimes e mail signups or particular gives that require exiting to work together with the web page. Disable or exchange them with smaller, much less onerous parts.
Google’s Search Central weblog cites “extreme adverts” as a unfavourable person expertise, though it doesn’t specify what it considers extreme, solely “adverts that distract from or intrude with the principle content material.”
Regardless, the hurt of large popups and extreme adverts goes past the useful content material replace. They impression readers. Keep away from them regardless of Google.