ChatGPT often links to sources when answering prompts. Traffic from those clicks is typically high-converting in my testing. Unfortunately, ChatGPT frequently hallucinates URLs and sends visitors to nonexistent pages.
A study released this month by Ahrefs found ChatGPT 5 links to error pages nearly three times more than does Google Search.
To be sure, traffic thus far from ChatGPT is less than 5% for most sites. But it’s still a good idea to monitor ChatGPT-generated 404 errors and adjust the pages accordingly. With declining Google Search traffic, “saving” visits is paramount.
Address the problem in three steps:
- Track 404 “page not found” URLs in Google Analytics 4.
- Create helpful 404 pages for visitors from hallucinated URLs.
- Set up 301 redirects only for broken URLs that generate traffic.
I’ll explain the first step in this article.
Track in Google Analytics
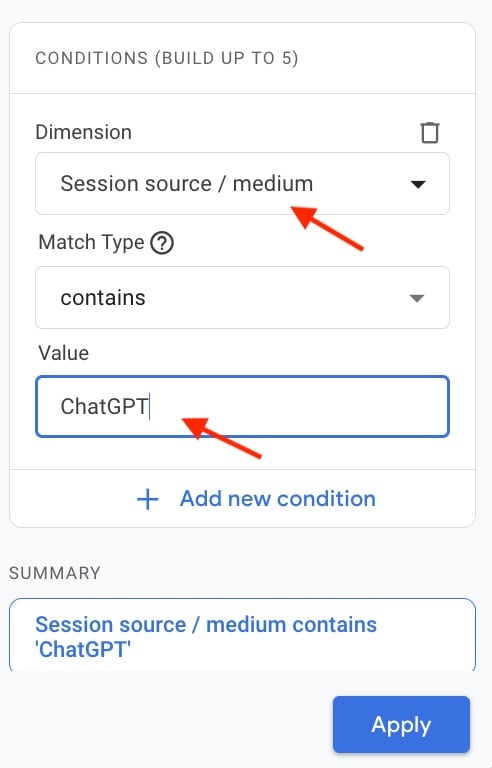
Filter Google Analytics reports to URLs with traffic from ChatGPT:
- Go to “Engagement” > “Pages and screens” to view all pages with traffic for the designated period.
- Select “Page titles and screen class” above the list of pages.
- Click “Add filter” above the graph.
- Select “Session source/medium” as the dimension.
- Select “Contains” and type “ChatGPT.”
- Click “Apply.”
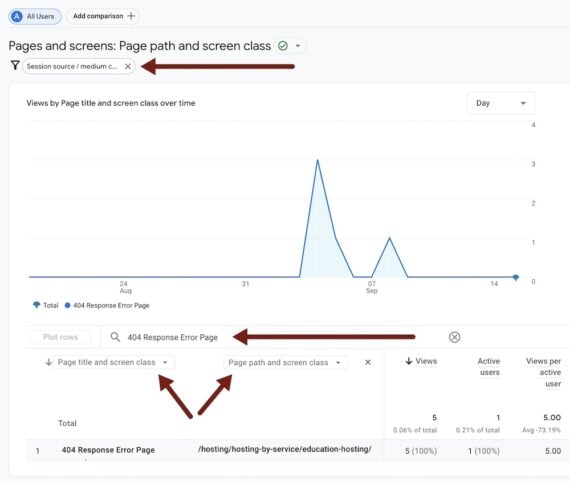
Now your list is filtered to pages with traffic from ChatGPT.
Next, narrow the list to error pages:
- Go to your site and open all the ChatGPT-filtered pages above.
- Note the title of pages with 404 errors (Ctrl+D on Windows; Command+D on Mac). In my case, the title was “404 Response Error Page.”
Then return to Google Analytics:
- Type the error page title in the search bar above the list of pages with traffic from ChatGPT. Add “Page path and screen” class as a secondary dimension to view the hallucinated URLs.
- Bookmark the URL of this report and check from time to time.