Google has strived for years to diversify search outcomes. But it nonetheless incessantly returns two or extra natural listings per question from the identical web site, which search optimizers name “area clustering.”
On desktop outcomes, the second clustered itemizing is indented.
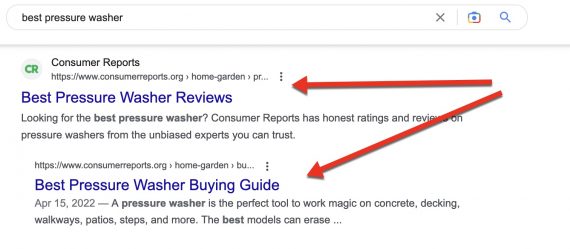
On desktop outcomes, the second clustered itemizing is indented.
But it surely’s not indented on cell.
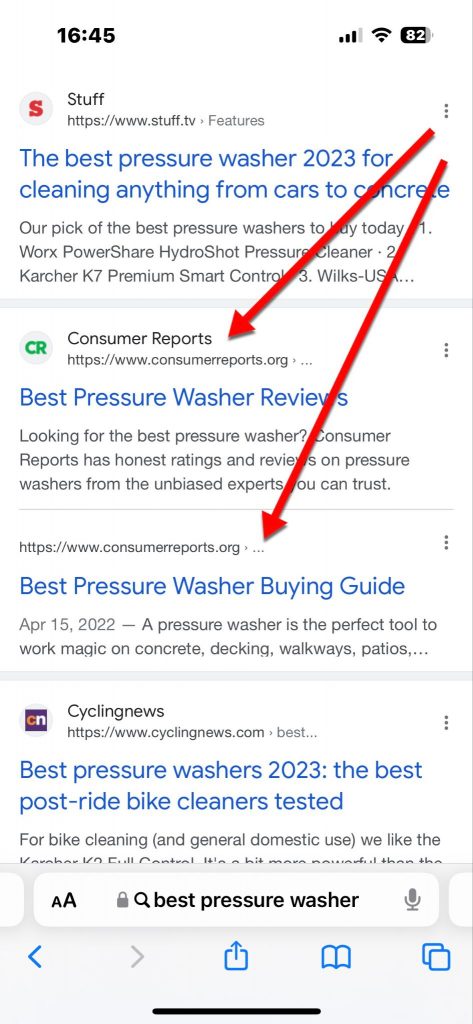
Clustered listings aren’t indented on cell search outcomes.
Having two listings for a single question presumably produces extra clicks. Thus optimizers typically search methods to realize these outcomes. I do know of no documentation from Google on the subject. However anecdotally it seems Google makes use of clustering in three situations.
Twin meanings. A key phrase question might have twin meanings, prompting Google to provide a list for each. An instance is a question for “framing.”
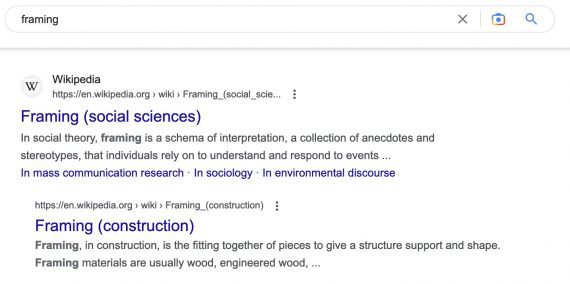
“Framing” has twin meanings, prompting Google to provide a cluster from Wikipedia addressing every one.
Uncertain of intent. Google could cluster outcomes when it’s unsure of the searcher’s intent — business or informational. An instance is a seek for “french drain.”
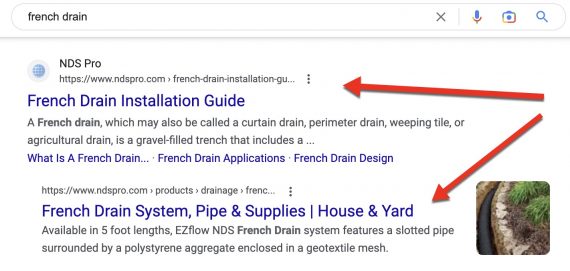
A searcher for “french drain” could possibly be seeking to buy or searching for set up recommendation.
Comparable URLs. A web site might have a number of related pages for a single question, equivalent to related merchandise or classes. Google might ship two or extra of these pages to assist the searcher. Goal, for instance, gives “floating wall cabinets” and “wooden floating cabinets.” Thus Google has clustered each URLs for the question “floating cabinets.”
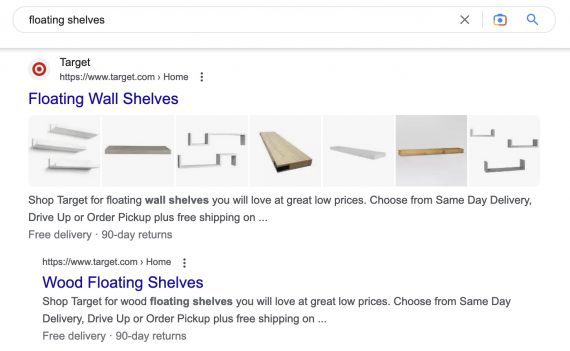
Goal has two pages appropriate for a search of “floating cabinets”: one for partitions and the opposite for wooden.
In different phrases, Google continues to cluster domains when it helps searchers, regardless of asserting search-result diversification in 2019.
However optimizing key phrases for clusters dangers one web page competing towards one other.
Cannibalizing Key phrases
“Key phrase cannibalization” means optimizing two or extra pages of a web site for a similar search time period. It’s a doubtful tactic for 2 causes.
First, it might confuse Google’s algorithms, uncertain which web page to index and rank. And complicated Google is dangerous. I’ve typically seen informational weblog pages rank the place the searcher’s intent is clearly business.
Second, the follow splits key phrase fairness between a number of pages, diluting them and thus “cannibalizing” search engine marketing efforts.
For years, I’ve monitored key phrase cannibalization in search engine marketing audits. Websites with high-ranking pages keep away from it. Thus a logical query is optimize for area clustering with out cannibalizing key phrases.
One possibility is “intent optimization.”
Intent Optimization
A web site can optimize for searchers’ intent, not simply their key phrases. There’s nothing flawed with creating two pages for a similar subject: one for business intent and the opposite for informational.
For instance, a seek for “tile paint” might apply to purchasing paint or utilizing it. Therefore optimizing for that question would come with a product class web page with a number of buy choices and an informational information or article.
The pages ought to hyperlink to one another to handle searchers’ wants. Key phrases for buying might embrace “on sale,” “straightforward to make use of,” and related, whereas informational phrases could be “” and “widespread errors.”
Creating seasonal how-to guides to complement business pages may help with area clustering. The guides might listing present and costume concepts and decor choices, as examples.
Regardless, optimizing for clustered domains dangers key phrase cannibalization. I might not try it for a web page already rating at or close to the highest for a goal key phrase. Plus, clustered outcomes come at a value: they seldom seem for place 1.

